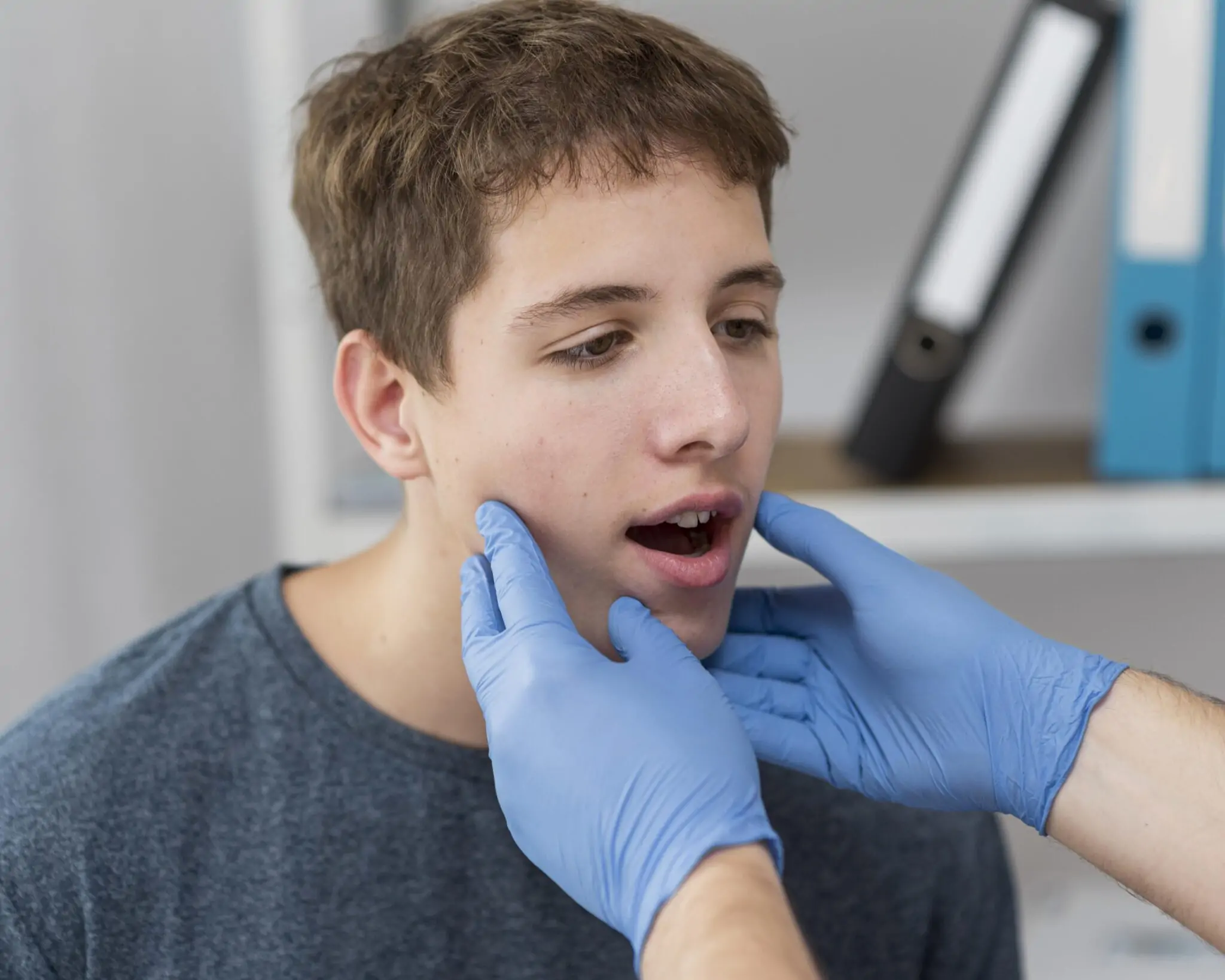
Maxillofacial traumas are generally injuries that affect the soft bones and tissues in the jaw and facial area. Maxillofacial traumas, which may occur as a result of sports injuries, traffic accidents, acts of violence, falls, and workplace accidents, affect physical functions such as speaking and eating. They also cause negative effects on physical appearance. These injuries must be treated by specialist maxillofacial surgeons, and surgical intervention and a long rehabilitation process are required. Prof. Dr. Celal Çandırlı carries out an effective treatment process in such injuries with the correct treatment methods.
Bu Yazımızda Neler Var :
What Does Maxillofacial Taumas Mean?
The maxillofacial region is defined as the area outside the nervous system of the skull, that is, excluding the brain, brainstem, cerebellum, and spinal cord. More clearly, it includes facial regions such as the cheeks, eyes, jaw, and nose.
Serious injuries may occur in this area due to accidents or various external factors. These injuries are defined as maxillofacial traumas. Surgical procedures carried out in the maxillofacial area are called maxillofacial surgery.
What Are Maxillofacial Traumas?
Maxillofacial traumas are known as a medical issue that is increasing day by day. When correct and effective treatment is not applied, maxillofacial traumas may lead to the risk of death or disability in some patients.
These injuries occur in areas such as the face and skull that do not have protective features against external impacts; they may be seen as many different traumatic injuries. They may appear in different forms ranging from simple cuts and abrasions to soft tissue loss and crush injuries, facial and jaw injuries, and complex injuries characterized by various bone fractures. If maxillofacial traumas are to be explained, they include:
- Nasal fractures
- Zygomatic bone fractures
- Mandibular fractures
- Orbital floor fractures
- Maxillary fractures
- Tooth fractures
- Sinus injuries
- Supraorbital region fractures
- Alveolar fractures
- Nasoethmoidal fractures
Modern Treatment Methods for Maxillofacial Traumas
Examination for maxillofacial traumas generally begins with medical history. First of all, the location of the maxillofacial trauma must definitely be questioned. In this way, the possible location of the facial bone fracture is identified.
| Examination Method | Description |
| Inspection | Edema, hematoma, ecchymosis and, if present, functional losses are observed. The condition of bone integrity and whether there is crepitation are examined. |
| Radiographic Examinations | A highly effective method in diagnosing facial bone fractures. With these examinations, the shape and location of the fracture and whether there is displacement at the fracture ends can easily be revealed. |
| Caldwell View | With this examination, the orbital bone, frontal bone, lateral wall of the maxillary sinus, and zygomaticofrontal sutures are visualized. Orbital floor fractures can also be detected. |
| Waters View | Traumas such as the maxilla, maxillary sinus, and zygomatic arch and bones can be observed with this examination. |
| Fronto-Occipital Anteroposterior View | Injuries such as the mandible, upper and lower dental arches, nasal septum, nasal floor, and hard palate are revealed with this examination. |
| Reverse Waters and Mento-Occipital View | This method is useful in examining the zygomatic bone, orbit, and maxillary sinus. |
After all these examinations are performed, the treatment method to be applied to the patients is planned through a comprehensive and systematic algorithm. In general, the treatment process for maxillofacial traumas is carried out in the form of surgical intervention. Afterwards, a long rehabilitation process begins for the patients.
In such maxillofacial traumas, urgent and correct treatment is necessary. Because negative conditions that cause permanent facial deformities and respiratory problems may occur. In such a situation, you may contact Prof. Dr. Celal Çandırlı.
What Is a Maxillary Fracture?
The maxilla region is the widest bone in the middle part of the face and is known as the area where trauma is most frequently seen. This region is extremely important in terms of the functions of sensory organs.
As a result of various traumas, maxillary fractures may occur, and due to these fractures, disorders in speaking, chewing, and swallowing functions and facial deformities may be seen. Within the scope of orthognathic surgery, various treatment methods are applied to correct traumatic fractures.
Le Fort Fracture Classification
Maxillary fractures, which generally occur during traffic accidents, are classified in different ways. So, how are these traumatic fractures classified?
- Partial alveolar fracture
- Le Fort I fracture
- Le Fort II fracture
- Le Fort III fracture
If detailed information is to be given regarding Le Fort fractures:
- Le Fort I Fracture is also called a “floating palate fracture.” It generally involves the palatal bone and the lower parts of the sphenoid and pterygoid bones.
- Le Fort II Fracture is also called a pyramidal fracture of the maxilla. The fracture line passes through the nasal bones, zygomaticomaxillary sutures, and the inferior orbital rim.
- Le Fort III Fracture is also called craniofacial dysjunction. If the facial trauma is severe, serious consequences may arise.
What Is a Zygomatic Bone Fracture?
One of the facial traumas that occur due to causes such as home, workplace, and traffic accidents is the zygomatic bone fracture. This condition negatively affects both the function and aesthetic appearance of the face. As a result of a zygomatic bone fracture, areas such as the upper and lower jaw bones, nose, periorbital region, cheekbones, and forehead may be damaged.
Various treatments are applied for zygomatic fractures by maxillofacial surgeons. The severity and condition of the fracture affect the treatment. Conservative treatments are applied in mild fractures. However, in advanced fractures, surgical methods are preferred.
In the surgical method, the zygomatic fracture is corrected and the bone is restored to its anatomical position. In this procedure, stabilizing medical materials such as zygomatic implants, plates, screws, and wires are used.
Frequently Asked Questions
The most frequently asked questions about maxillofacial traumas are as follows:
1 – What Are Maxillofacial Fractures?
Maxillofacial surgery, also called oral and maxillofacial surgery, is a field that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the mouth, face, neck, and jaw region. Various maxillofacial traumas may occur in this area. Maxillofacial fractures resulting from traumas are corrected with facial implants and other modern treatment methods.
2 – What Does Maxillofacial CT Mean?
It is a type of dental X-ray that uses a special scanner to capture images in the related area. Thanks to this X-ray, maxillofacial traumas and problems are diagnosed correctly.
3 – What Are Major Traumas?
Severe falls and injuries, traffic accidents, physical assaults, sports injuries, wars, and natural disasters are sources that cause physical trauma in humans. Due to these events, a physical impact occurs in the body. In other words, maxillofacial traumas, tissue damage, and bleeding can be given as examples of serious consequences.
4 – What Does Maxillofacial Mean in Medicine?
In medical literature, maxillofacial traumas are defined as fractures that occur in the mouth, jaw, neck, and facial region as a result of various accidents.
5 – Where Is the Maxillofacial Region?
The maxillofacial region, where maxillofacial traumas occur, is the area outside the parts of the skull such as the brainstem, spinal cord, brain, and cerebellum. In other words, it refers to areas such as the cheeks, eyes, nose, and jaw.
Bir Cevap Yaz